Lead is toxic to humans, even in very small amounts; unfortunately, lead can be found in many household materials and often, lead poisoning victims are children. Lead introduced into the human body remains there: over time, lead building up in the body can result in toxic results including compromised mental health and physical development as well as death.
Lead poisoning happens over a period of months or years; it is a slow, silent poison of the body that may go unnoticed until severe damage has already occurred. Homes built before 1950 are most likely to contain lead-based paint. Any home with lead-soldered plumbing can contaminate the home’s water supply.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC):
4,000,000 homes in the United States have lead poisoning dangers
500,000 American children under the age of 5 have blood lead levels over 5 micrograms (the CDC recommended level for medical action)
The two highest risk groups for lead poisoning are:
1. Children under the age of 6 years
2. Workers who are exposed on the job to lead sources – including lead paint, lead dust, car batteries, etc.
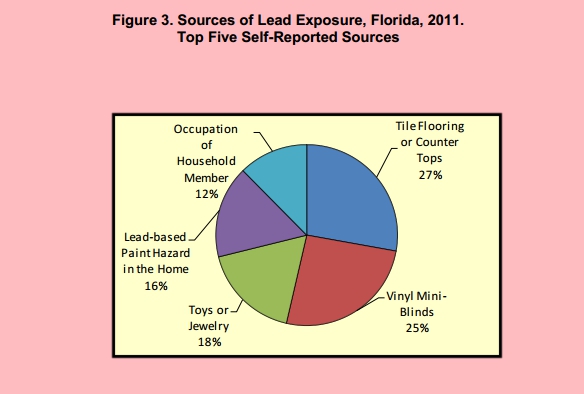
Contamination sources include:
- Lead-based paint (particularly house paint before 1978)
- Lead-filled dust
- Air contaminated with lead
- Water contaminated with lead
- Soil contaminated with lead
- Toys painted before 1976
- Furniture painted before 1976
- Toys made in countries other than the United States
- Plumbing, pipes, and faucets with lead solder, allowing lead to contaminate drinking water
- Soil contaminated by accumulated car exhaust
- Pewter pitchers and dinnerware.
- Storage batteries.
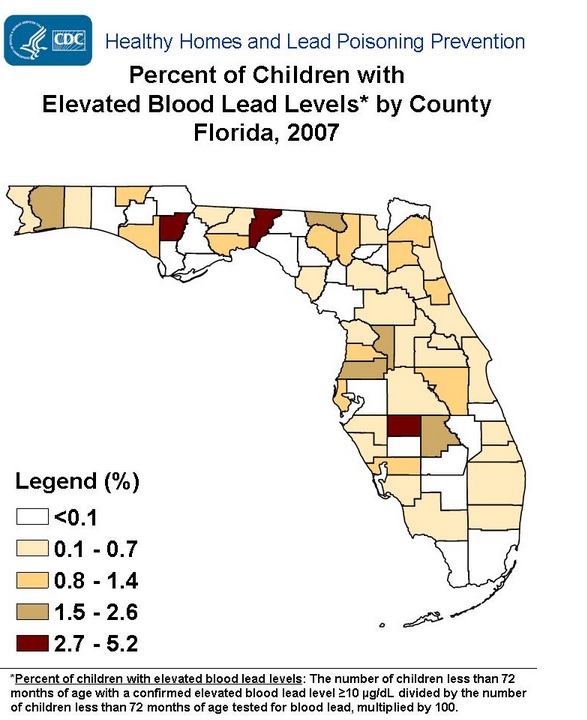
Lead Poisoning in Florida – Children
According to the Florida Department of Health:
- There has been a 48 percent (48%) decline in the rate of new cases per children screened was observed between 2007 (2.3 cases per 1,000 children screened) and 2011 (1.2 cases per 1,000 children screened).
- The decline in the statewide Florida lead poisoning rate was most noticeable between 2007 and 2008 (30 percent) and 2008 and 2009 (31 percent).
- Compared to previous years, there was an decrease (14 percent) in the case rate from 2010 to 2011.
- Although the number of new cases declined consistently from 2007 to 2009, there was an increase (34%) in the number of newly identified lead poisoned cases from 2009 to 2010 (190 and 254 respectively). This may be due to an increase in the identification of cases in high-risk zip codes and among high-risk populations.
- In 2011, there was a 22% decrease in the number of newly identified lead poisoned cases in comparison to 2010. This decline in cases may be due to enhanced primary prevention activities in identifying and recommending services for the elimination of lead poisonings amongst high-risk children.
- In 2011, the 12-23 months of age group category was noted to have the highest risk for lead poisoning. Specifically, it was found that this age group category represented the largest percent (32 percent) of new cases.
- Over the past five years, most reported new cases have BLLs ranging from 10 to14 μg/dL.
- In 2011, 71 percent (45 cases) of reported new cases (63 cases), 12-23 months of age, had BLLs within the 10 to14 μg/dL range.
From 2000 – 2011, the Miami-Dade County Health Department recorded 250 instances of elevated blood lead levels.
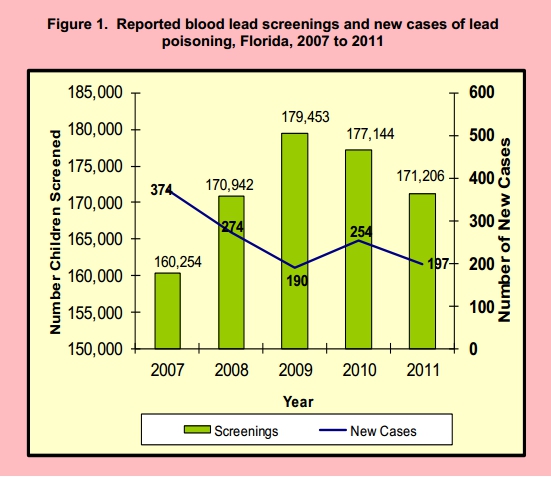
From 2007 to 2011, the Florida Department of Health found:
- Children screened for lead poisoning in Florida increased by 7% percent.
- Lead poisoning cases in Florida declined by 47% percent.
- The number of lead poisoning cases in Florida fell from 374 in 2007 to 197 in 2011.
- In 2011, most lead poisoning cases in Florida were babies between 12 and 23 months old (32 percent).
- In 2011, babies under the age of 23 months old tested for lead poisoning also had the highest amount of lead in their blood (testing > 20ug/dl).
Broward County Cases of Children With Lead Poisoning
2007 – 51 cases of lead poisoning
2008 – 21 cases of lead poisoning
2009 – 14 cases of lead poisoning
2010 – 26 cases of lead poisoning
2011 – 20 cases of lead poisoning
Miami- Dade County Cases of Children With Lead Poisoning
2007 – 108 cases of lead poisoning
2008 – 89 cases of lead poisoning
2009 – 49 cases of lead poisoning
2010 – 78 cases of lead poisoning
2011 – 43 cases of lead poisoning
Palm Beach County Cases of Children With Lead Poisoning
2007 – 18 cases of lead poisoning
2008 – 19 cases of lead poisoning
2009 – 19 cases of lead poisoning
2010 – 16 cases of lead poisoning
2011 – 15 cases of lead poisoning
